Hamas: Understanding the Palestinian Islamic Resistance Movement in 2025
Hamas: Understanding the Palestinian Islamic Resistance Movement in 2025
Hamas, officially known as the Islamic Resistance Movement, has been at the center of Middle Eastern politics since its founding in 1987. This comprehensive guide explores what Hamas is, its origins, objectives, and its significant role in the ongoing Israeli-Palestinian conflict.
What is Hamas? Definition and Overview
Hamas is a Sunni Islamist Palestinian nationalist political organization founded in Gaza Strip in December 1987. The name "Hamas" is an acronym for "Harakat al-Muqawama al-Islamiyya" (Islamic Resistance Movement) in Arabic, which also means "zeal" or "strength."
The organization operates both as a political entity governing the Gaza Strip since 2007 and maintains a military wing known as the Al-Qassam Brigades. Hamas has been designated as a terrorist organization by the United States, European Union, Israel, and several other countries, while other nations view it as a legitimate resistance movement.
Origins and Historical Background of Hamas
Hamas emerged from the Palestinian branch of the Muslim Brotherhood during the First Intifada in 1987. The organization was founded by Palestinian Islamic scholar Sheikh Ahmed Yassin, who established it as an offshoot of his earlier Islamic charity, Mujama al-Islamiya, which had been active in Gaza since 1973.
Interestingly, Israel initially provided discreet support to Hamas in its early years as a counterbalance to the secular Palestine Liberation Organization (PLO), hoping to prevent the creation of a unified Palestinian state.
Hamas Goals and Political Objectives
Hamas's primary objectives have evolved significantly since 1987:
Original 1988 Charter Goals
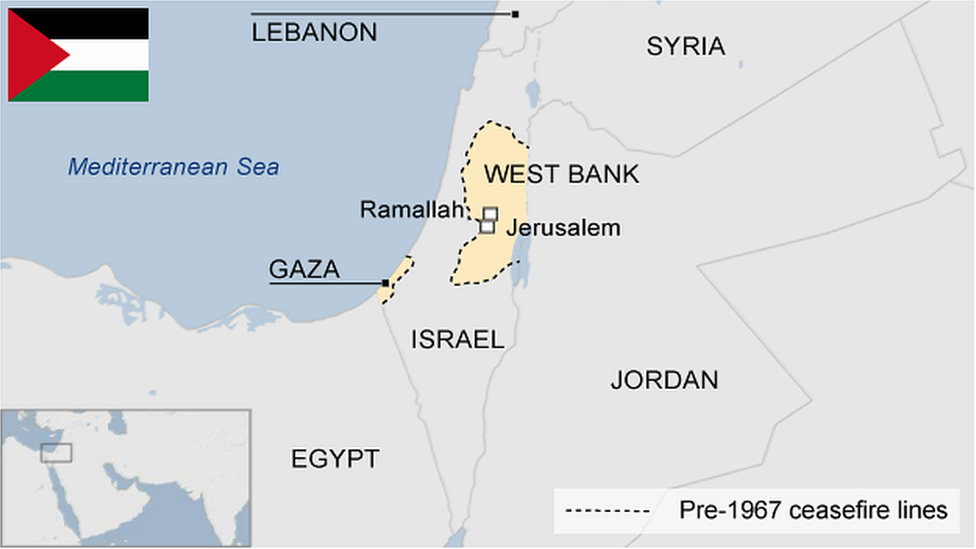
The original Hamas charter called for the establishment of an Islamic Palestinian state encompassing all of historic Palestine, from the Jordan River to the Mediterranean Sea, effectively replacing Israel entirely.
Modern 2017 Charter Updates
In May 2017, Hamas released an updated charter that signaled important policy shifts:
- Acceptance of a Palestinian state based on 1967 borders (Gaza Strip, West Bank, and East Jerusalem)
- Distinction between opposing Zionism and antisemitism
- Support for Palestinian resistance against Israeli occupation
- Rejection of any permanent recognition of Israel
Hamas Leadership Structure and Organization
Hamas operates through several key organizational branches:
Political Bureau
Currently led by a temporary council following the deaths of previous leaders Ismail Haniyeh (assassinated July 2024) and Yahya Sinwar (killed October 2024). The political leadership is primarily based in Qatar and Turkey.
Military Wing - Al-Qassam Brigades
The armed wing responsible for military operations, rocket attacks, and tunnel networks. Before the 2023 conflict, Hamas was estimated to command approximately 30,000 fighters.

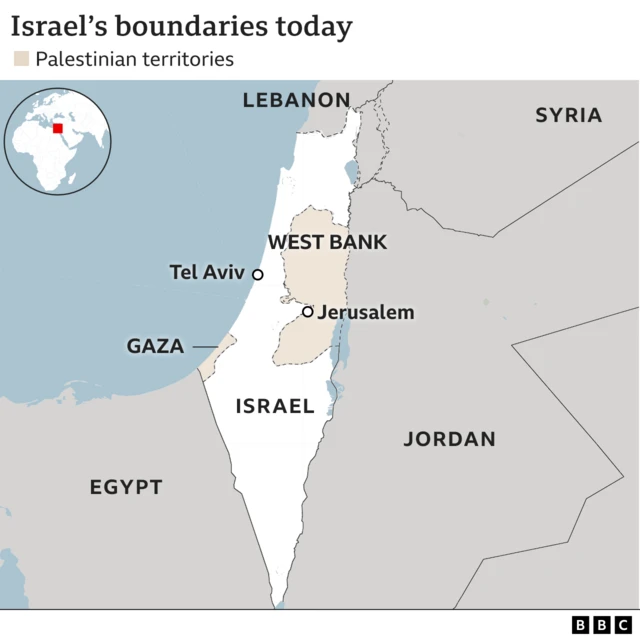
Hamas Governance of Gaza Strip
Since winning Palestinian legislative elections in 2006 and subsequently taking control of Gaza in 2007, Hamas has governed the territory's 2.3 million residents. This governance includes:
- Civil administration and public services
- Educational institutions and healthcare systems
- Security forces and law enforcement
- Economic management under blockade conditions
The organization faces significant challenges governing Gaza due to the Israeli-Egyptian blockade imposed after their takeover, which restricts movement of people and goods.
Major Conflicts and Military Actions
Hamas has been involved in several major conflicts with Israel:
- 2008-2009 Gaza War: First major military confrontation
- 2012 Gaza Conflict: Eight-day operation
- 2014 Gaza War: 50-day conflict with significant casualties
- 2021 Gaza Crisis: 11-day escalation
- 2023-Present: Ongoing war following October 7 attacks
The October 7, 2023 attack marked the deadliest attack on Israel in its history, resulting in approximately 1,200 Israeli deaths and 250 hostages taken to Gaza.
International Relations and Support
Hamas maintains relationships with several regional powers:
Key Allies
- Iran: Primary financial and military supporter
- Qatar: Financial aid and diplomatic headquarters
- Turkey: Political support and regional backing
International Designation
While designated as a terrorist organization by the US, EU, UK, Canada, and others, some countries and international bodies view Hamas as a legitimate resistance movement representing Palestinian aspirations.
Frequently Asked Questions About Hamas
Is Hamas the same as the PLO?
No, Hamas and the PLO are different organizations. The PLO, led by Fatah, is secular and has historically been the main representative of Palestinians internationally. Hamas is Islamist and emerged as a rival to the PLO's secular approach.
Does Hamas want a two-state solution?
Hamas's position is complex. While its 2017 charter accepts a Palestinian state within 1967 borders, it doesn't recognize Israel's right to exist. Hamas leaders have proposed long-term truces (hudna) but maintain their ultimate goal of liberating all historic Palestine.
How is Hamas funded?
Hamas receives funding from multiple sources including Iran (estimated hundreds of millions annually), Qatar, taxes and duties in Gaza, charitable donations, and various business enterprises.
What is Hamas's relationship with other Palestinian factions?
Hamas has a complex relationship with other Palestinian groups. While it cooperates with some factions against Israel, it has been in political competition with Fatah since 2007, when it took control of Gaza after defeating Fatah forces.
Current Status and Future Outlook
As of 2025, Hamas faces significant challenges following the ongoing conflict with Israel that began in October 2023. The organization's military capabilities have been severely degraded, its leadership structure disrupted, and Gaza's infrastructure largely destroyed.
Despite these setbacks, Hamas continues to maintain governance over Gaza and remains a key player in any future Palestinian political settlement. The organization's evolution from a purely rejectionist movement to one that has shown some flexibility on territorial compromise reflects the complex realities of Palestinian politics.
Understanding Hamas is crucial for anyone seeking to comprehend the Israeli-Palestinian conflict and Middle Eastern politics. As both a militant organization and governing authority, Hamas represents the aspirations and frustrations of many Palestinians while remaining controversial due to its methods and ultimate objectives.
Share This Article
Found this analysis helpful? Share this comprehensive guide to Hamas with others interested in understanding Middle Eastern politics and the Israeli-Palestinian conflict. Knowledge sharing helps promote informed discussions about complex geopolitical issues.
