Health Insurance Options: Your Complete Guide to Coverage in the USA
Health Insurance Options: Your Complete Guide to Coverage in the USA
Navigating the health insurance landscape in the United States can feel overwhelming, but understanding your options is the first step toward securing the right coverage for you and your family. Whether you're exploring employer-sponsored plans, marketplace options, or government programs, this comprehensive guide breaks down everything you need to know about health insurance in America.
With healthcare costs continuing to rise, having the right health insurance isn't just about compliance—it's about protecting your financial future and ensuring access to quality medical care when you need it most.
Understanding Different Types of Health Insurance Coverage
Employer-Sponsored Health Insurance
The most common form of coverage in the United States, employer-sponsored insurance allows you to share premium costs with your employer. These group plans typically offer comprehensive benefits and lower out-of-pocket costs compared to individual plans. If your employer offers health insurance, this is often your most cost-effective option.
ACA Marketplace Plans (Obamacare)
The Affordable Care Act created health insurance marketplaces where individuals and families can shop for coverage. These plans are categorized into metal tiers—Bronze, Silver, Gold, and Platinum—based on how costs are shared between you and the insurer. Depending on your income, you may qualify for premium tax credits that significantly reduce your monthly costs.
Government Programs: Medicare and Medicaid
Medicare serves Americans age 65 and older, plus certain younger people with disabilities. Medicaid provides low-cost or free coverage for eligible low-income individuals and families. Each state administers its own Medicaid program with varying eligibility requirements, so check your state's specific guidelines.
Short-Term Health Insurance
These temporary plans fill coverage gaps when you're between jobs or waiting for other coverage to begin. While more affordable, short-term plans offer limited benefits and don't cover pre-existing conditions. They're best used as a bridge solution, not long-term coverage.
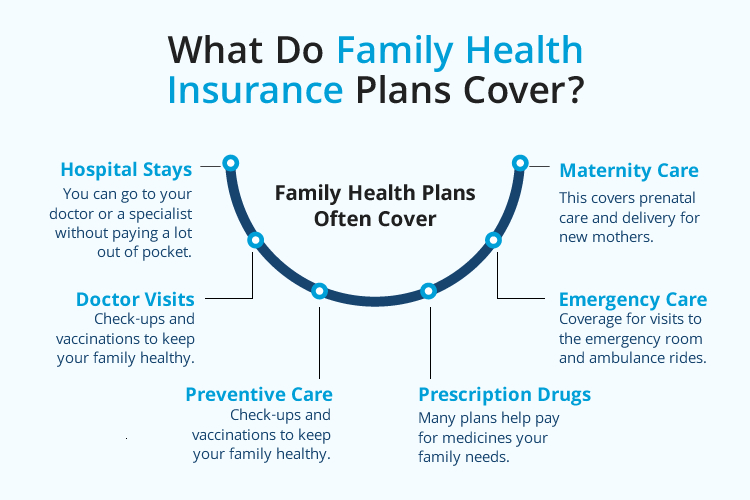
Key Health Insurance Terms You Need to Know
Understanding insurance terminology helps you make informed decisions and avoid surprise costs. Here are the essential terms every consumer should know:
Premium: Your monthly payment to maintain coverage, regardless of whether you use healthcare services. Think of it like a subscription fee for access to care.
Deductible: The amount you pay out-of-pocket before your insurance starts covering costs. Plans with higher deductibles typically have lower premiums, and vice versa.
Copayment and Coinsurance: Your share of costs for covered services. Copays are fixed amounts (like $30 per doctor visit), while coinsurance is a percentage of the total cost (like 20% of a hospital stay).
Out-of-Pocket Maximum: The cap on what you'll pay annually. Once you reach this limit, your insurance covers 100% of covered services for the rest of the year. This protects you from catastrophic medical expenses.
How to Choose the Right Health Insurance Plan
Assess Your Healthcare Needs
Consider how often you visit doctors, any ongoing medical conditions, and prescription medication needs. If you rarely need medical care, a high-deductible plan with lower premiums might work. If you have chronic conditions requiring regular care, comprehensive coverage with higher premiums but lower out-of-pocket costs may be more economical.
Check Provider Networks
Ensure your preferred doctors and hospitals accept the plan you're considering. HMO plans typically require you to choose a primary care physician and get referrals for specialists, while PPO plans offer more flexibility but at higher costs.
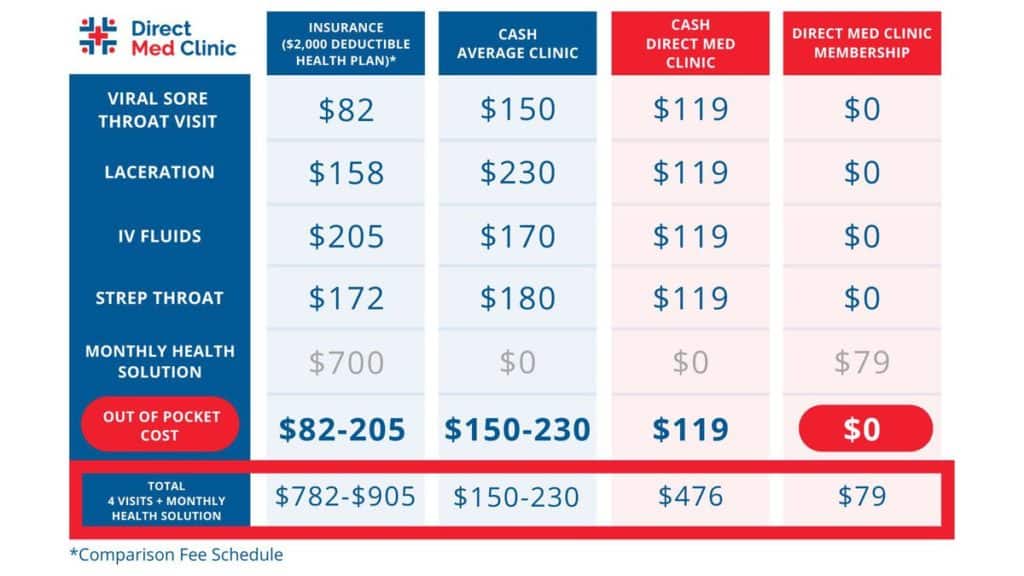
Compare Total Costs, Not Just Premiums
A plan with a low monthly premium might seem attractive, but factor in deductibles, copays, and coinsurance. Calculate potential annual costs based on your expected healthcare usage to find the plan that offers the best overall value.
When Can You Enroll in Health Insurance?
For ACA marketplace plans, the Open Enrollment Period typically runs from November 1 through January 15. Missing this window means you'll need to wait until next year unless you qualify for a Special Enrollment Period due to life events like losing other coverage, getting married, having a baby, or moving to a new state.
Employer-sponsored insurance usually has its own enrollment period, typically in the fall. Short-term plans, dental coverage, and vision insurance can generally be purchased year-round.
Maximizing Your Health Insurance Benefits
Take full advantage of preventive care services, which are covered at 100% under ACA-compliant plans. Annual checkups, screenings, and vaccinations cost you nothing and can detect health issues early when they're most treatable.
Consider Health Savings Accounts (HSAs) if you have a high-deductible health plan. HSAs offer triple tax advantages: contributions are tax-deductible, growth is tax-free, and withdrawals for qualified medical expenses aren't taxed. Unlike Flexible Spending Accounts (FSAs), HSA funds roll over year after year.
Frequently Asked Questions
What happens if I don't have health insurance?
While the federal penalty for not having health insurance has been eliminated, some states impose their own penalties. More importantly, going uninsured leaves you vulnerable to devastating medical bills and limits your access to preventive care.
Can I keep my doctor with any health insurance plan?
It depends on the plan's network. PPO plans typically offer the most flexibility to see out-of-network providers, though at higher costs. Always verify your doctors participate in a plan's network before enrolling.
How do I know if I qualify for financial assistance?
Most people earning between 100-400% of the federal poverty level qualify for premium tax credits through the ACA marketplace. Visit HealthCare.gov or contact a licensed insurance agent to determine your eligibility based on household size and income.
What's the difference between HMO and PPO plans?
HMO plans require you to choose a primary care physician and get referrals for specialists, but typically cost less. PPO plans offer more flexibility to see any provider without referrals but come with higher premiums and out-of-pocket costs.
Take Control of Your Health Coverage Today
Choosing the right health insurance is one of the most important financial decisions you'll make. By understanding your options, comparing plans carefully, and considering your family's healthcare needs, you can find coverage that provides both protection and peace of mind.
Don't wait until a medical emergency strikes to think about insurance. Whether you're shopping during open enrollment or experiencing a qualifying life event, take time to evaluate your options thoroughly. The right health insurance plan is an investment in your health and financial security.
Found this guide helpful? Share it with family and friends who need help understanding their health insurance options! Together, we can help more Americans make informed decisions about their healthcare coverage.