La Niña 2024-2025: Complete Guide to the Climate Phenomenon Impacting the United States
La Niña 2024-2025: Complete Guide to the Climate Phenomenon Impacting the United States
Key Takeaway: La Niña conditions have returned in late 2024, bringing significant weather changes across the United States through early 2025. This comprehensive guide explains everything Americans need to know about this climate phenomenon.
Table of Contents
- What is La Niña?
- Current La Niña Conditions 2024-2025
- How La Niña Affects the United States
- Regional Weather Effects
- La Niña vs El Niño: Key Differences
- Winter 2024-2025 Outlook
- Frequently Asked Questions
What is La Niña? Understanding the Climate Phenomenon
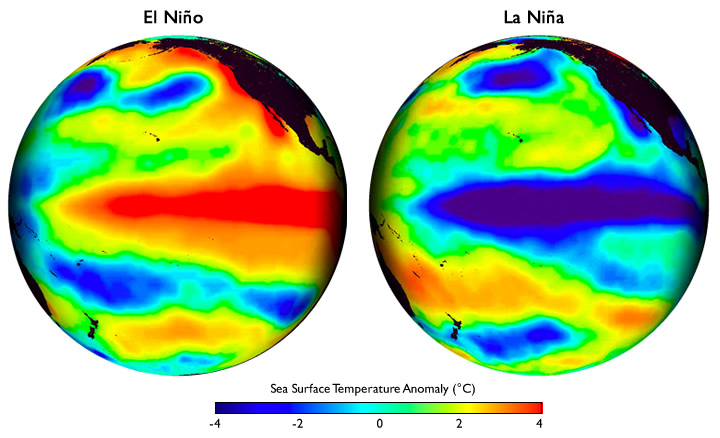 La Niña, meaning "Little Girl" in Spanish, represents one phase of the El Niño-Southern Oscillation (ENSO) climate pattern. This phenomenon occurs when sea surface temperatures in the central and eastern tropical Pacific Ocean become significantly cooler than average—at least 0.5°C (0.9°F) below normal.
During La Niña events, stronger-than-usual trade winds push warm surface water westward toward Asia, allowing cold, nutrient-rich water to rise to the surface along the coasts of Peru and Ecuador. This process, called upwelling, creates the characteristic cooling pattern that defines La Niña conditions.
La Niña, meaning "Little Girl" in Spanish, represents one phase of the El Niño-Southern Oscillation (ENSO) climate pattern. This phenomenon occurs when sea surface temperatures in the central and eastern tropical Pacific Ocean become significantly cooler than average—at least 0.5°C (0.9°F) below normal.
During La Niña events, stronger-than-usual trade winds push warm surface water westward toward Asia, allowing cold, nutrient-rich water to rise to the surface along the coasts of Peru and Ecuador. This process, called upwelling, creates the characteristic cooling pattern that defines La Niña conditions.
The Science Behind La Niña
La Niña episodes typically develop between June and August, reach peak intensity during winter months (December through February), and gradually weaken during spring. These events generally last 9-12 months but can occasionally persist for two to three years, creating what meteorologists call "multi-year" La Niña events.Current La Niña Conditions: 2024-2025 Status
According to the latest reports from NOAA's Climate Prediction Center, La Niña conditions officially returned in late 2024. Sea surface temperatures in the critical Niño-3.4 region have dropped below the -0.5°C threshold, with computer models forecasting these conditions to persist through December 2025 to February 2026. This marks the return of La Niña after a period of neutral conditions, potentially bringing significant weather changes across the United States during the crucial winter months.How La Niña Affects United States Weather Patterns
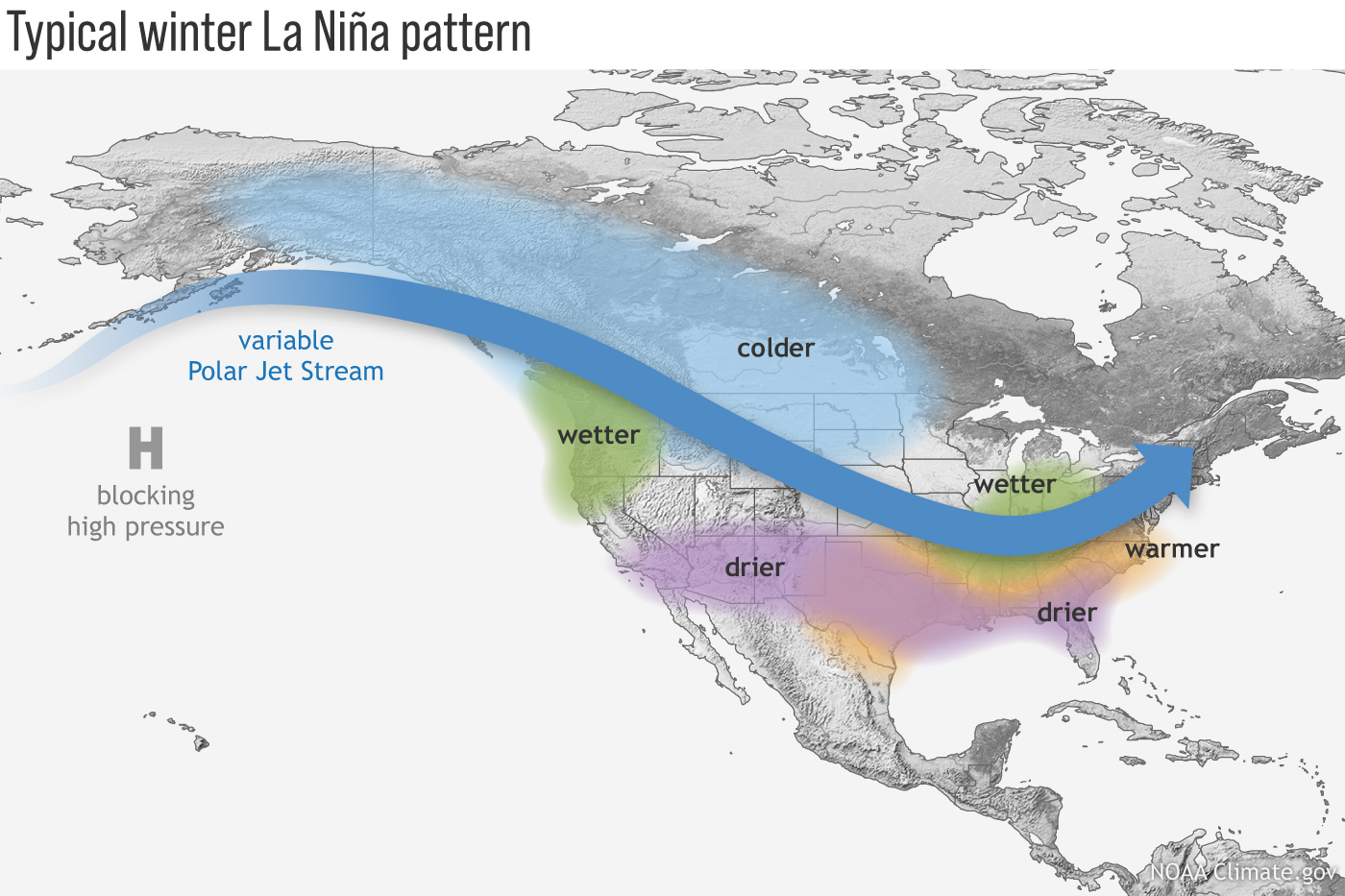 La Niña's influence on American weather occurs primarily through its impact on the jet stream—the high-altitude river of air that steers weather systems across North America. During La Niña events, the Pacific jet stream shifts northward, creating distinct regional weather patterns.
La Niña's influence on American weather occurs primarily through its impact on the jet stream—the high-altitude river of air that steers weather systems across North America. During La Niña events, the Pacific jet stream shifts northward, creating distinct regional weather patterns.
Jet Stream Modifications
The northward displacement of the jet stream during La Niña creates a characteristic wave-like flow pattern across North America. This configuration tends to:- Direct storm systems along more northern tracks
- Allow Arctic air masses easier access to central and eastern United States
- Create persistent high-pressure ridges over the southern states
- Enhance moisture transport from the Gulf of Mexico to northern regions
Regional Weather Effects Across America
Northern United States and Great Lakes
The northern tier of states typically experiences La Niña's most pronounced effects: Temperature: Colder than normal winter temperatures, particularly in the Upper Midwest and Great Lakes region Precipitation: Increased snowfall and overall precipitation, with some areas seeing 20-40% above normal snowfall Storm Activity: More frequent and intense winter stormsSouthern United States
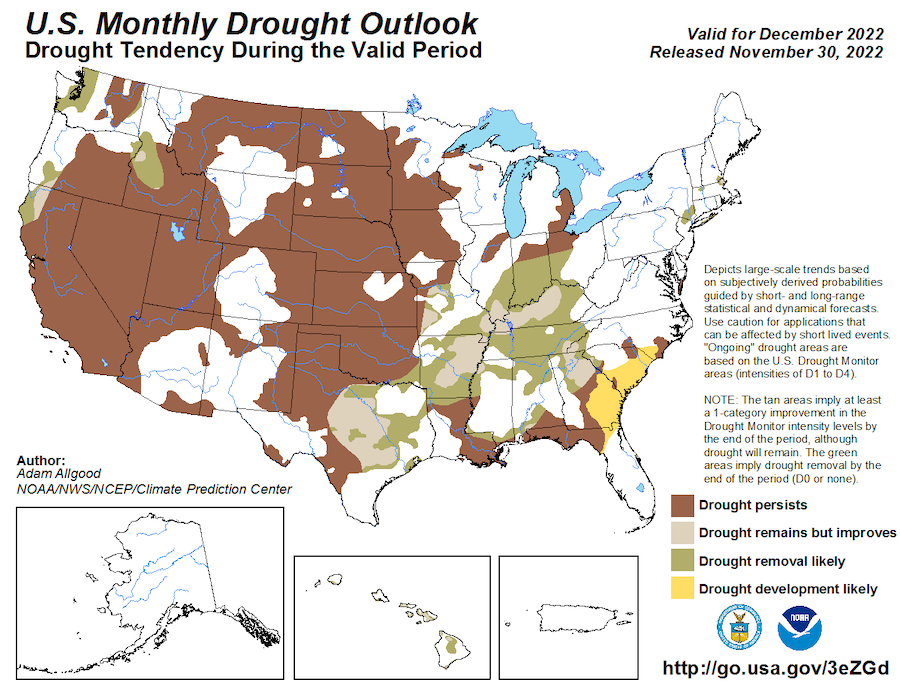 Southern regions from Texas to Florida typically see opposite effects:
Temperature: Warmer and drier than normal conditions
Precipitation: Below-average rainfall, increasing drought risks
Severe Weather: Reduced tornado activity due to less atmospheric instability
Southern regions from Texas to Florida typically see opposite effects:
Temperature: Warmer and drier than normal conditions
Precipitation: Below-average rainfall, increasing drought risks
Severe Weather: Reduced tornado activity due to less atmospheric instability
Western United States
The West Coast experiences varied impacts depending on the La Niña's strength: Pacific Northwest: Wetter than normal conditions, beneficial for water supplies California: Northern regions may see increased precipitation, while southern areas remain drier Mountain West: Enhanced snowpack in northern mountains, crucial for water resourcesLa Niña vs El Niño: Understanding the Key Differences
While La Niña and El Niño are opposite phases of the same climate pattern, their impacts on the United States differ dramatically:| Aspect | La Niña | El Niño |
|---|---|---|
| Pacific Ocean | Cooler than normal | Warmer than normal |
| Northern US Winter | Colder, snowier | Warmer, drier |
| Southern US Winter | Warmer, drier | Cooler, wetter |
| Hurricane Activity | More active seasons | Less active seasons |
Winter 2024-2025 Outlook for the United States
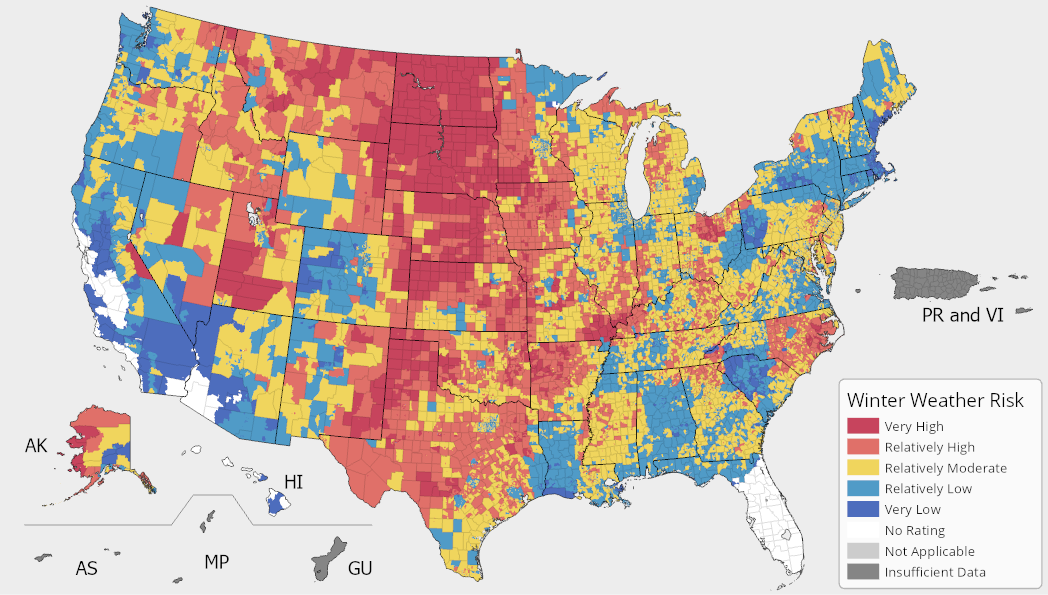 Based on current La Niña conditions, meteorologists expect the following patterns for winter 2024-2025:
Based on current La Niña conditions, meteorologists expect the following patterns for winter 2024-2025:
Temperature Expectations
- Great Lakes and Upper Midwest: 60-70% chance of below-normal temperatures
- Northern Plains: Increased likelihood of prolonged cold spells
- Southeast and Gulf Coast: Above-normal temperatures expected
- Southwest: Near-normal to slightly above-normal temperatures
Precipitation Forecasts
- Pacific Northwest: Above-normal precipitation, beneficial for drought recovery
- Northern Rockies: Enhanced snowpack accumulation expected
- Ohio Valley: Increased winter precipitation likely
- Southern Plains: Below-normal precipitation, continuing drought concerns
Frequently Asked Questions About La Niña
How long will the current La Niña last?
Current forecasts suggest La Niña conditions will persist through winter 2024-2025, with a transition to neutral conditions expected by spring 2025. However, some models indicate the possibility of continuation into late 2025.
Does La Niña make winters colder everywhere in the US?
No, La Niña affects different regions differently. While northern states typically experience colder winters, southern states often see warmer than normal conditions. The effects depend on how La Niña alters the jet stream pattern.
How does La Niña affect energy costs?
La Niña can significantly impact energy costs. Colder northern winters increase heating demand and costs, while warmer southern conditions may reduce heating needs but increase cooling costs in unseasonably warm periods.
Can La Niña affect agriculture in the United States?
Yes, La Niña significantly impacts agriculture through temperature and precipitation changes. Northern growing regions may benefit from increased moisture, while southern agricultural areas face drought stress. Crop planning often considers La Niña forecasts.
Preparing for La Niña's Impact
Understanding La Niña's regional effects helps Americans prepare for seasonal weather changes. Northern residents should prepare for potentially harsh winter conditions, while southern areas should monitor drought conditions and water resources. Stay informed through NOAA's Climate Prediction Center updates and local National Weather Service forecasts for the most current information on La Niña's evolving impacts.Found this article helpful?
Share this comprehensive La Niña guide with friends and family to help them understand and prepare for the climate impacts ahead.