What is a Nor'easter? Complete Guide to East Coast Winter Storms
What is a Nor'easter? Complete Guide to East Coast Winter Storms
Quick Navigation:
Nor'easters are among the most powerful and dangerous winter storms that affect the United States East Coast. These massive weather systems can bring hurricane-force winds, heavy snowfall, torrential rain, and devastating coastal flooding from Georgia to Maine. Understanding what makes these storms so destructive is crucial for millions of Americans living in their path.
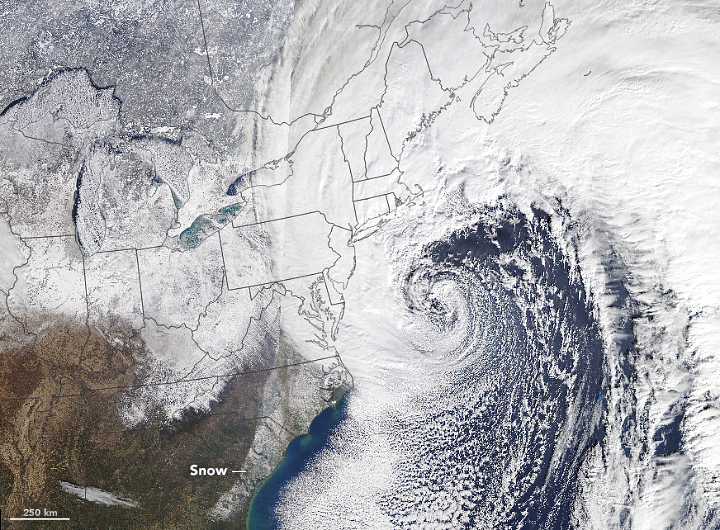
What is a Nor'easter?
A nor'easter is a large-scale storm system that develops along the East Coast of North America, characterized by strong winds blowing from the northeast direction over coastal areas. The National Weather Service defines these storms as extratropical cyclones that form when contrasting air masses collide near the Atlantic coastline.
These powerful weather systems typically develop within 100 miles of the East Coast, stretching from Georgia to New Jersey, before tracking northeastward toward New England and maritime Canada. The term "nor'easter" comes from the persistent northeast winds that pound coastal areas as these storms pass.
Some of the most famous nor'easters in American history include the Blizzard of 1888, the "Ash Wednesday" Storm of 1962, the New England Blizzard of 1978, and the March 1993 "Storm of the Century." These events have caused billions of dollars in damage and claimed numerous lives across the Northeast.
How Nor'easters Form and Develop
The formation of nor'easters requires specific atmospheric conditions that make the East Coast an ideal breeding ground for these storms:
The Perfect Storm Recipe
- Cold Arctic Air: The polar jet stream transports frigid air southward from Canada across the continental United States
- Warm Ocean Waters: The Gulf Stream keeps Atlantic coastal waters relatively warm during winter months
- Temperature Contrast: When cold air meets warm ocean water, it creates instability that fuels storm development
- Low Pressure Formation: This temperature difference causes clouds to form and low pressure systems to intensify

As these storms develop, they typically move northeastward along the coast, gaining strength and moisture from the warm Atlantic waters. The heavily populated "I-95 Corridor" from Washington D.C. to Boston bears the brunt of most nor'easter impacts due to its geographic position.
Nor'easter vs Hurricane: Key Differences
While both nor'easters and hurricanes can appear similar on satellite imagery, these storm types have fundamental differences:
Geographic Origins
- Hurricanes: Form over warm tropical waters near the equator
- Nor'easters: Develop along the cold northern Atlantic coast
Energy Sources
- Hurricanes: Powered by warm air and tropical heat
- Nor'easters: Thrive on cold air and temperature contrasts
Seasonal Timing
- Hurricanes: Peak activity June through November
- Nor'easters: Most common September through April

When Nor'easters Occur
While nor'easters can technically develop any time of year, they follow distinct seasonal patterns:
- Peak Season: September through April, with maximum intensity during winter months
- Most Severe: December through March when temperature contrasts are greatest
- Early Season: September-November storms often bring more rain than snow
- Late Season: March-April events can be particularly impactful due to warmer ground temperatures
Modern meteorological technology, including NOAA's GOES-16 satellite, continuously monitors atmospheric conditions to provide early warning of developing nor'easters, giving residents crucial time to prepare.
Weather Impacts and Dangers
Nor'easters pose multiple serious threats to life and property across the Eastern United States:
Wind Hazards
- Sustained winds often exceed 40-50 mph
- Wind gusts can reach hurricane-force levels (74+ mph)
- Power outages affecting millions of customers
- Downed trees and structural damage
Precipitation Threats
- Heavy Snow: Accumulations of 1-3 feet in a single storm
- Blizzard Conditions: Combined with winds, creating whiteout conditions
- Torrential Rain: Several inches in coastal areas, causing flooding
- Ice Storms: Freezing rain creating hazardous conditions
Coastal Flooding
- Storm surge pushing seawater inland
- Beach erosion and property damage
- Overwash of barrier islands
- Damage to coastal infrastructure
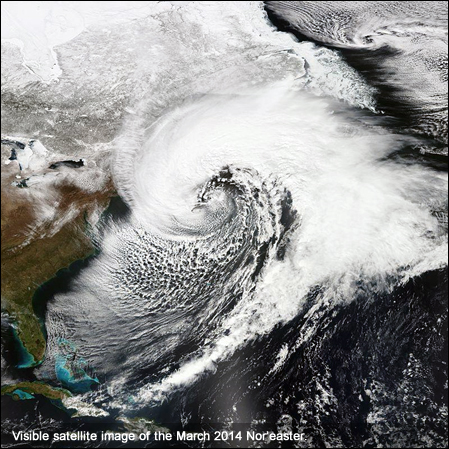

Nor'easter Preparation and Safety Tips
Proper preparation can significantly reduce the impact of nor'easters on your family and property:
Before the Storm
- Emergency Kit: Stock 3-7 days of food, water, medications, and supplies
- Power Preparedness: Charge devices, consider backup generators, have flashlights and batteries
- Home Protection: Secure outdoor furniture, clear gutters, check heating systems
- Vehicle Readiness: Fill gas tanks, check antifreeze, have emergency car kit
- Stay Informed: Monitor weather.gov and local forecasts for updates
During the Storm
- Stay indoors and avoid unnecessary travel
- Never drive through flooded roads
- Use generators outdoors only to prevent carbon monoxide poisoning
- Conserve phone battery for emergencies
- Keep away from downed power lines

Frequently Asked Questions
How long do nor'easters typically last?
Most nor'easters persist for 12-36 hours as they track along the coast. However, their impacts can be felt for several days before and after the main event, especially in terms of coastal flooding and cleanup efforts.
Which states are most affected by nor'easters?
The most impacted states include Maine, New Hampshire, Vermont, Massachusetts, Rhode Island, Connecticut, New York, New Jersey, Pennsylvania, Delaware, Maryland, Virginia, and North Carolina. The I-95 corridor from Washington D.C. to Boston sees the most frequent impacts.
Can nor'easters produce tornadoes?
While uncommon, nor'easters can occasionally spawn tornadoes, particularly along their southern and eastern edges where wind shear is greatest. These are typically weak, short-lived tornadoes but can still cause localized damage.
How far inland do nor'easter effects reach?
While coastal areas face the worst impacts, nor'easters can affect areas several hundred miles inland. Heavy snow, high winds, and power outages are common well into interior New England, New York, and Pennsylvania during major events.
Stay Weather Aware and Prepared
Nor'easters remain one of the most significant weather threats facing the Eastern United States. These powerful storms have shaped American history and continue to impact millions of lives each winter season. By understanding how they form, when they're most likely to occur, and how to prepare properly, you can protect yourself and your family from their devastating effects.
Remember to always stay informed through official weather sources like the National Weather Service, and never underestimate the power of these remarkable storm systems. Climate change research suggests that while nor'easters may become less frequent, the strongest ones are likely to become more intense, making preparation even more critical for East Coast residents.
Share This Vital Weather Information
Help keep your community prepared for nor'easters! Share this comprehensive guide with friends, family, and neighbors along the East Coast. Knowledge saves lives when severe weather strikes. Forward this article via email, post it on social media, or discuss it with your local emergency management office.