Military Pay 2025: Complete Guide to Salary, Benefits, and Allowances
Military Pay 2025: Complete Guide to Salary, Benefits, and Allowances

Military compensation in 2025 includes significant pay increases and comprehensive benefits that extend far beyond basic salary. Understanding your total military compensation package is crucial for financial planning and maximizing your benefits as a service member.
Basic Military Pay Structure
Basic pay forms the foundation of military compensation and is received by all service members regardless of branch. This taxable income is determined by two primary factors: your pay grade (rank) and years of service. The military uses a standardized pay scale that applies to all branches including the Army, Navy, Air Force, Marines, Coast Guard, and Space Force.
For 2025, an E-1 (lowest enlisted rank) receives $2,319 monthly in basic pay, while a seasoned E-6 with over 10 years of service earns $4,585.20 per month. Officers start at $3,998.40 for new O-1s, with experienced O-4s earning $9,075 monthly. These amounts increase automatically based on time in service and promotions.
2025 Pay Increases and Charts
The 2025 military pay increase brings significant improvements, especially for junior enlisted personnel. Most service members received a 4.5% pay raise, but junior enlisted ranks (E-1 through E-4) and some E-5s received a substantial 14.5% increase to address retention and recruitment challenges.
Implementation Timeline
- January 2025: 4.5% increase for all ranks
- April 2025: Additional 10% for junior enlisted (totaling 14.5%)
This targeted increase recognizes that junior enlisted members often face financial hardships early in their careers. The additional raise helps bridge the gap between military and civilian entry-level wages, improving military competitiveness in the job market.
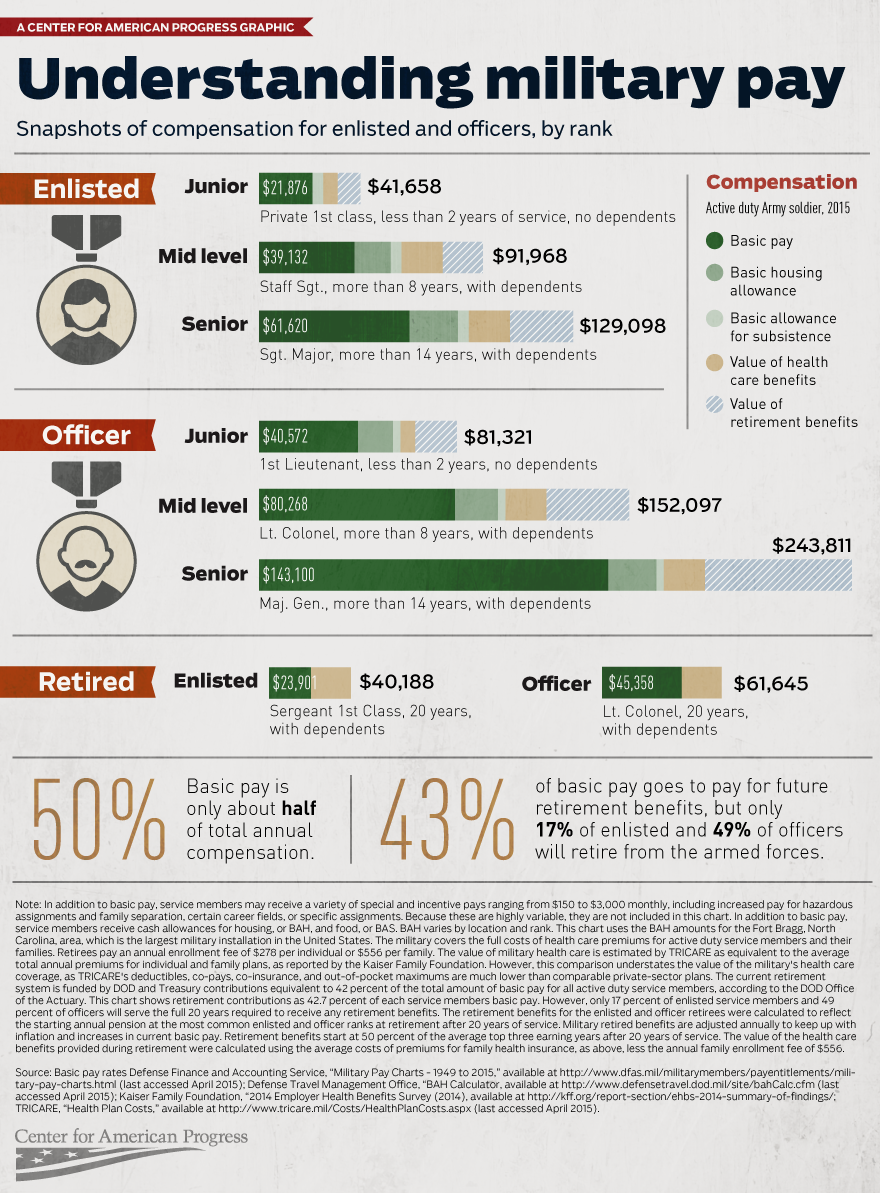
Military Allowances and Benefits
Military allowances often comprise the largest portion of your total compensation and are generally tax-free, providing significant financial advantages. The two primary allowances are Basic Allowance for Housing (BAH) and Basic Allowance for Subsistence (BAS).
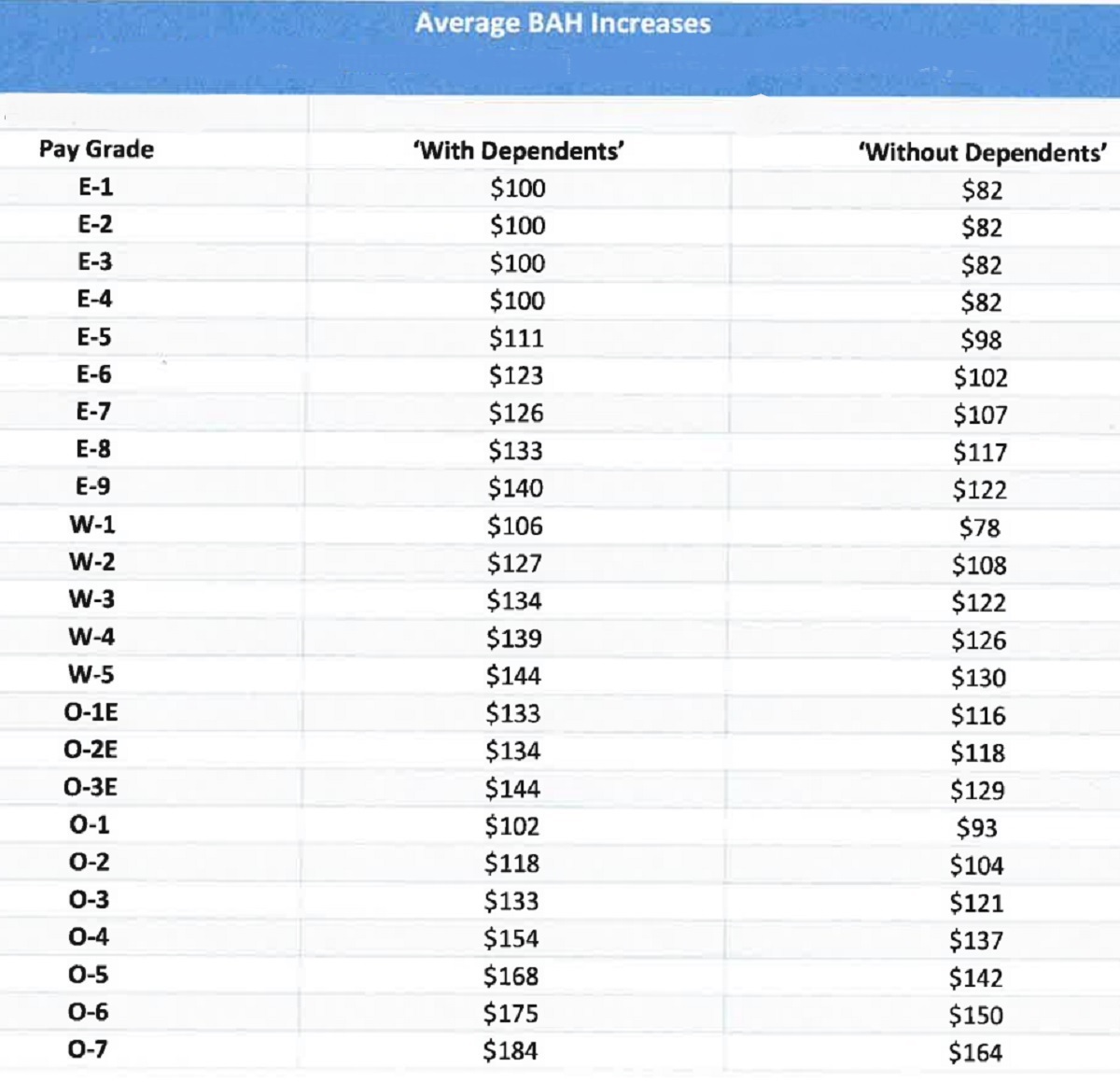
Basic Allowance for Housing (BAH)
BAH varies significantly based on your rank, dependency status, and duty location. Service members stationed in high-cost areas like San Francisco or New York receive substantially more BAH than those in lower-cost regions. For example, an E-5 with dependents in San Francisco receives over $4,000 monthly in BAH, while the same rank in a rural area might receive $1,200.
Basic Allowance for Subsistence (BAS)
BAS covers meal expenses and is standardized across all ranks and locations. For 2025, enlisted members receive $460.25 monthly, while officers receive $322.72. This allowance is provided regardless of whether you use base dining facilities.
Special and Incentive Pay
The military offers numerous special pays for specific qualifications, duties, or conditions. These payments recognize additional skills, dangers, or hardships associated with certain positions.

Common Special Pays Include:
- Flight Pay: $150-$840 monthly for aviators
- Hazardous Duty Pay: $150-$275 monthly for dangerous assignments
- Combat Pay: Tax exclusion for combat zone service
- Family Separation Allowance: $250 monthly during extended separations
- Hardship Duty Pay: Additional compensation for difficult assignments
These payments can significantly increase your total compensation, sometimes adding $500-$1,000 or more to your monthly pay depending on your specialty and assignment.
How to Calculate Your Military Pay
Your total military compensation extends beyond basic pay to include allowances, special pays, and benefits. The military uses Regular Military Compensation (RMC) to calculate your total package, which includes:
- Basic Pay (taxable)
- Basic Allowance for Housing (BAH) - tax-free
- Basic Allowance for Subsistence (BAS) - tax-free
- Tax savings from non-taxable allowances
To accurately compare military pay to civilian wages, multiply your tax-free allowances by approximately 1.25 to account for their tax-exempt status. This calculation often reveals that military compensation is more competitive than basic pay alone suggests.
Reading Your Leave and Earnings Statement (LES)
Your monthly LES provides detailed information about your pay, deductions, and leave balance. Key sections include entitlements (what you earn), deductions (taxes, insurance), and your net pay. Review your LES monthly to ensure accuracy and track your financial progress.
Frequently Asked Questions
When do military pay increases take effect?
Military pay increases typically take effect January 1st each year and are reflected in the first pay period of the year. The 2025 junior enlisted increase took effect April 1st as an exception.
Are military allowances taxable?
Most military allowances, including BAH and BAS, are not taxable. This tax-free status significantly increases the value of your total compensation compared to equivalent civilian wages.
How is military pay determined?
Military pay is based on the Employment Cost Index, which tracks civilian wage increases. Congress may adjust these amounts, as they did for junior enlisted in 2025.
Do all military branches receive the same pay?
Yes, all military branches use the same basic pay scale. However, special pays and allowances may vary based on job specialty and duty assignment.
What should I do if my military pay is incorrect?
Contact your finance office immediately if you notice pay discrepancies. For most branches, call 1-888-332-7411. Coast Guard members should contact their unit administrative yeoman.
How do I access my military pay information online?
Use the myPay system at mypay.dfas.mil to view your Leave and Earnings Statement (LES), update personal information, and manage your pay account.